Back muscles, often overlooked, play a pivotal role in our daily lives, from maintaining proper posture to facilitating a wide range of physical activities. Understanding their anatomy, functions, and training methods is essential for overall well-being and optimal performance.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of back muscles, empowering readers with knowledge and practical strategies to enhance their back health and fitness.
As Mother’s Day approaches, it’s time to show our gratitude to the special women in our lives. Happy Mother’s Day to all the amazing moms out there.
Back Muscles: Overview

The back muscles, collectively known as the posterior chain, play a crucial role in maintaining posture, stabilizing the spine, and facilitating various movements. These muscles are essential for everyday activities such as walking, lifting objects, and bending over.
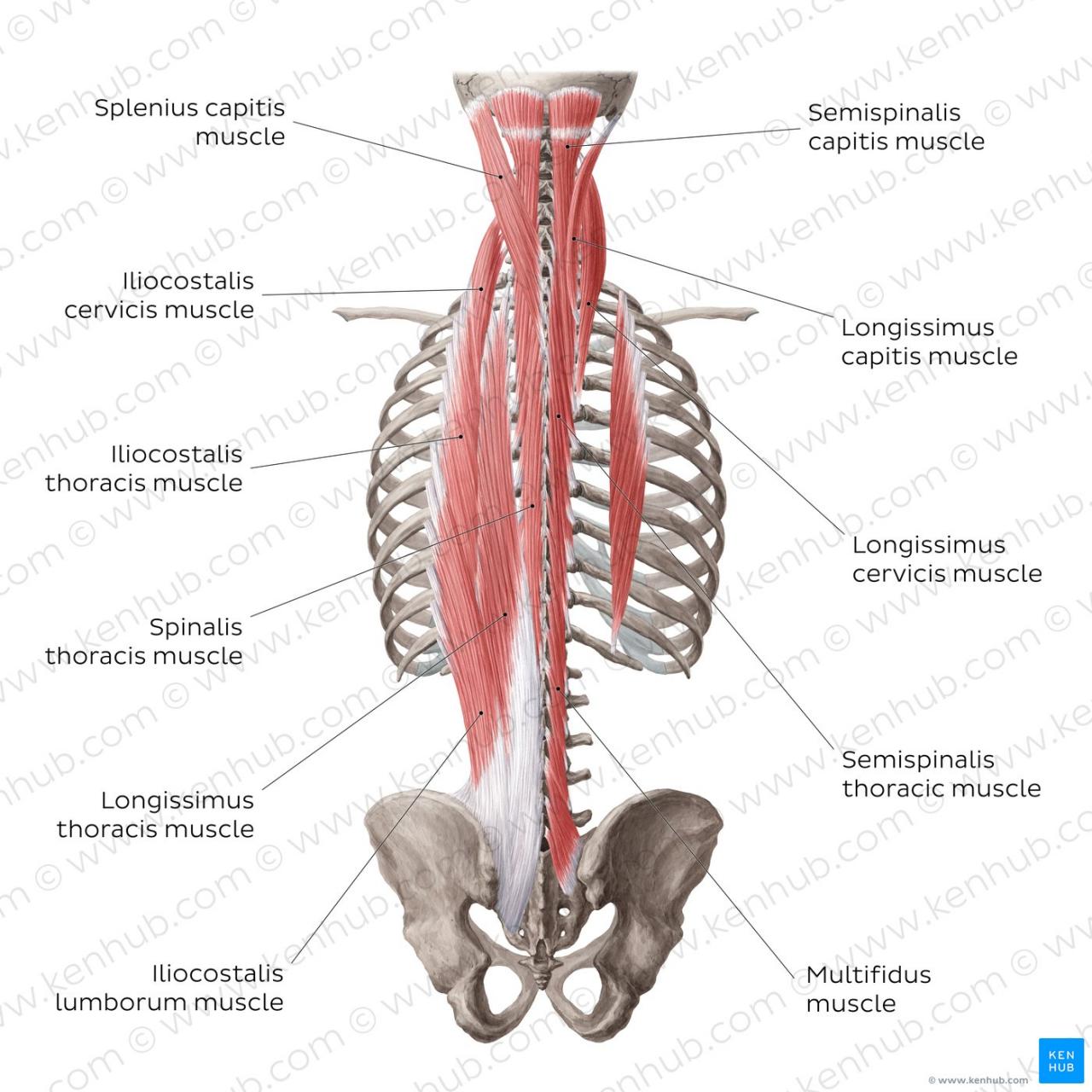
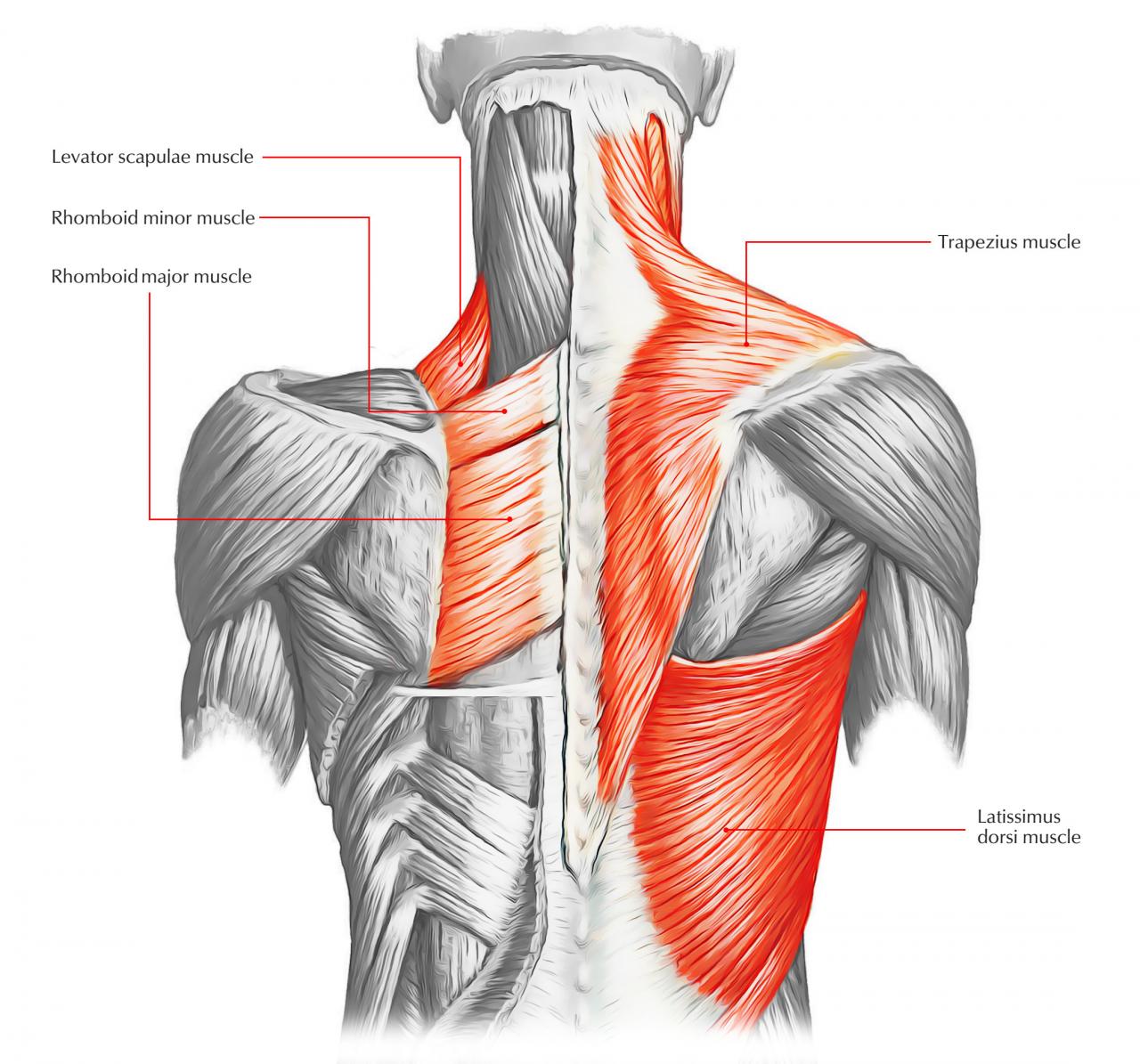
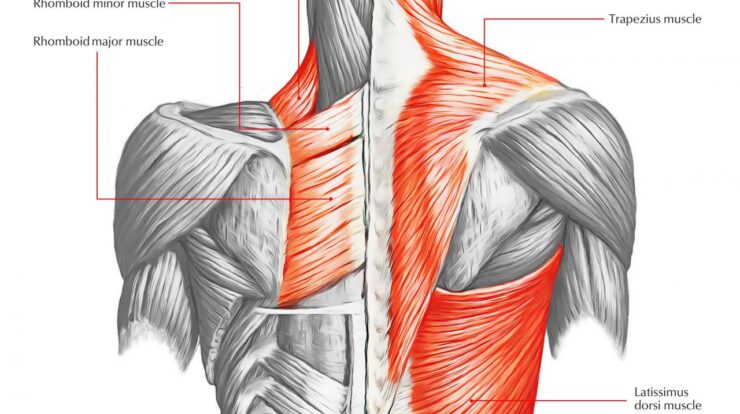
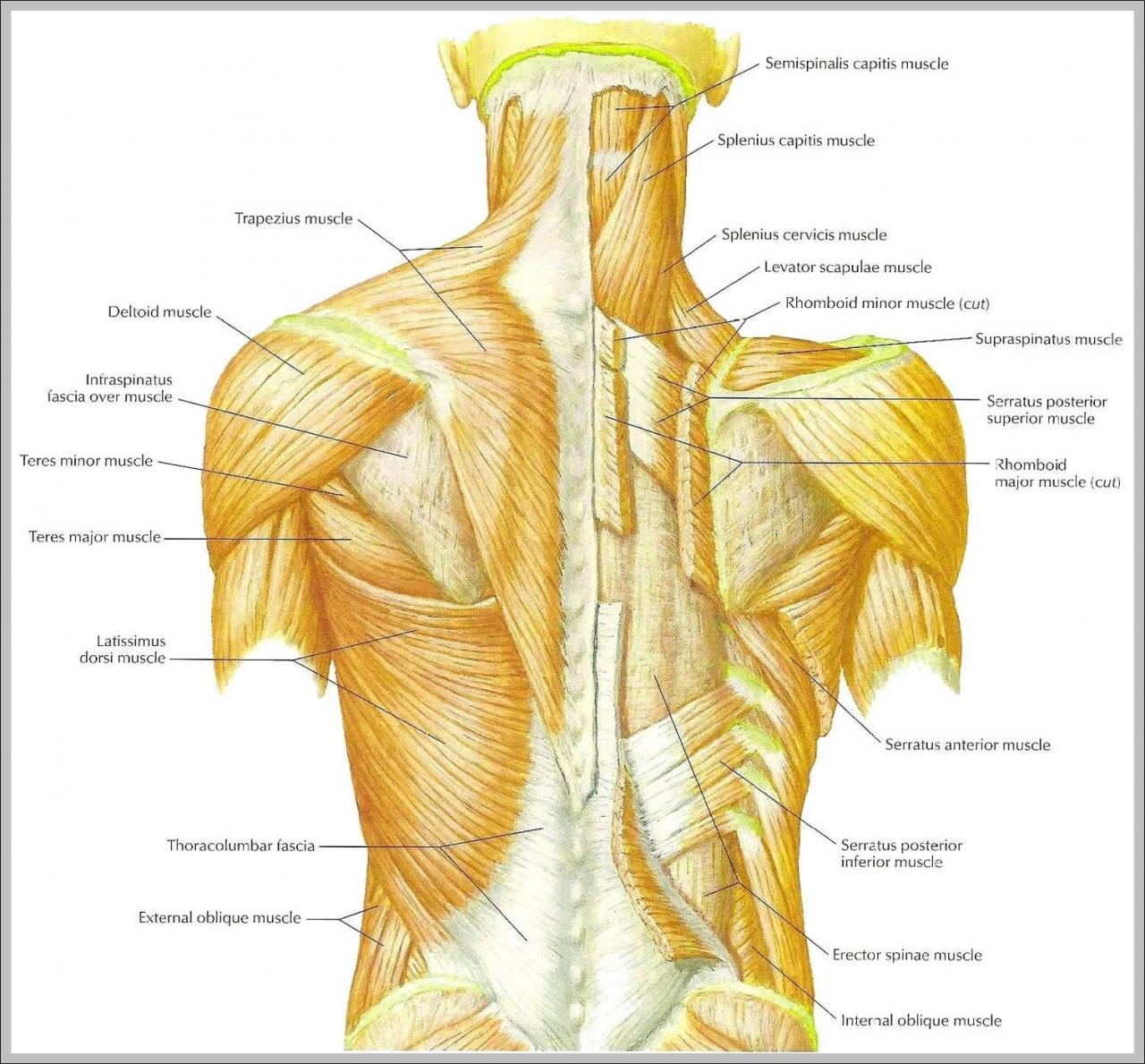
Major Back Muscles
- Trapezius: Upper back, extends from the base of the skull to the middle of the back
- Latissimus dorsi: Largest muscle in the back, originates from the lower spine and inserts into the humerus
- Rhomboids: Between the shoulder blades, responsible for shoulder retraction
- Erector spinae: Along the spine, supports the back and extends the spine
- Multifidus: Deep muscle group, stabilizes the spine and prevents excessive movement
Exercises for Strengthening Back Muscles
Incorporating exercises that target different back muscle groups is essential for overall back strength and health. A comprehensive workout plan should include both compound and isolation exercises.
| Exercise | Sets | Reps | Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barbell Row | 3-4 | 8-12 | Lie on a bench with your feet flat on the floor. Grasp a barbell with an overhand grip, shoulder-width apart. Pull the barbell towards your chest, keeping your back straight. |
| Lat Pulldown | 3-4 | 10-15 | Sit on a lat pulldown machine with your feet flat on the floor. Grasp the bar with an overhand grip, shoulder-width apart. Pull the bar down towards your chest, keeping your back straight. |
| Seated Cable Row | 3-4 | 12-15 | Sit on a cable row machine with your feet flat on the floor. Grasp the handles with an overhand grip, shoulder-width apart. Pull the handles towards your chest, keeping your back straight. |
| Back Extension | 3-4 | 15-20 | Lie on a back extension bench with your feet secured. Hold a weight plate behind your head. Raise your upper body, keeping your back straight. |
Back Muscle Anatomy and Physiology, Back muscles
The back muscles are composed of various muscle fibers that work together to provide strength, flexibility, and support. These muscles receive nerve innervation from the spinal cord and are supplied with blood by the dorsal aorta and its branches.
The structure of the back muscles allows for a wide range of movements, including extension, flexion, rotation, and lateral bending of the spine.
Back Muscle Injuries and Rehabilitation
Back muscle injuries can occur due to various factors, such as overuse, poor posture, or trauma. Common injuries include strains, sprains, and herniated discs.
The back muscles are a complex system of muscles that support the spine and help us move. These muscles can become stiff and tight, leading to back pain. If you’re experiencing back pain, it’s important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Once any medical issues have been ruled out, you can try some simple exercises to help relieve your pain. One effective exercise is to lie on your back and pull your knees to your chest. Hold this position for 30 seconds and repeat 10 times.
Rehabilitation for back muscle injuries involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Physical therapy can also help strengthen the back muscles and improve range of motion.
Strengthening and stretching back muscles can help prevent and alleviate back pain. Regular exercise and proper posture are essential for maintaining a healthy back.
Epilogue
In conclusion, back muscles are a complex and vital part of our musculoskeletal system, responsible for a multitude of essential functions. By understanding their anatomy, strengthening them through targeted exercises, and addressing imbalances, we can reap the benefits of improved posture, enhanced athletic performance, and reduced risk of injuries.
Clarifying Questions: Back Muscles
What are the major back muscles?
Wishing all the amazing moms out there a happy mother’s day to you too ! We appreciate all that you do for us. Thank you for your love, support, and guidance. We love you!
The major back muscles include the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, erector spinae, and spinalis.
Why is it important to have strong back muscles?
Strong back muscles support good posture, reduce the risk of back pain, improve balance, and enhance athletic performance.
What are some common back muscle injuries?
Back muscles are essential for maintaining good posture and supporting the spine. Weak or tight back muscles can lead to back pain and other health problems.
Common back muscle injuries include strains, sprains, and herniated discs.
The back muscles are a complex system of muscles that support the spine and help us move. These muscles can become stiff and tight, leading to back pain. If you’re experiencing back pain, it’s important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Once any medical issues have been ruled out, you can try some simple exercises to help relieve your pain.
How can I prevent back muscle injuries?
To prevent back muscle injuries, maintain good posture, warm up before exercising, lift weights properly, and avoid sudden or excessive movements.
Understanding how stiff and tight muscles can contribute to back pain is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies.